Introducing KX.AS.CODE
Over the last couple of years we have been working on a solution to provide our DevOps engineers with a playpit for learning, experimenting and innovating.
What started initially as a couple of static packer scripts, has since become a powerful dynamic framework for rolling out entire environment landscapes.
Most recently KX.AS.CODE was implemented at a major enterprise with the following goals (see use case example):
- Dynamic
on-demand provisioning/destruction of test environmentsin the public cloud - End-to-end developer workstation to
enhance local quality assurance capabilities
I like to describe KX.AS.CODE as follows.
KX.AS.CODE is a dynamic fully configurable and customizable
local cloud likeKubernetes environmentwith a number of functionalities you would expect to see when managing aKubernetes clusterin thecloud, including aningress controller,local and network storage services,load-balancer,domain services,identity management,secrets management, acertificate authority… and the best bit, you can launch it very quickly from our Jenkins based configurator and launcher. See the Quick Start Guide!Once the base services are up, KX.AS.CODE has a built in
App Storefor quickly installing additional solutions on top of the base outlined above, such asGitlab,Grafana,InfluxDB,SonarQube,NeuVector,IntelliJ IDEA,MSSQLServer… and many many more!As a bonus, you also get a
desktopfor easily accessing and managing deployed applications. The desktop makes things easier, but if you prefer, you can also deploy KX.AS.CODE without it.
For a more detailed description and a full guide to KX.AS.CODE, visit our documentation site.
Screenshots
Here some impressions of KX.AS.CODE.
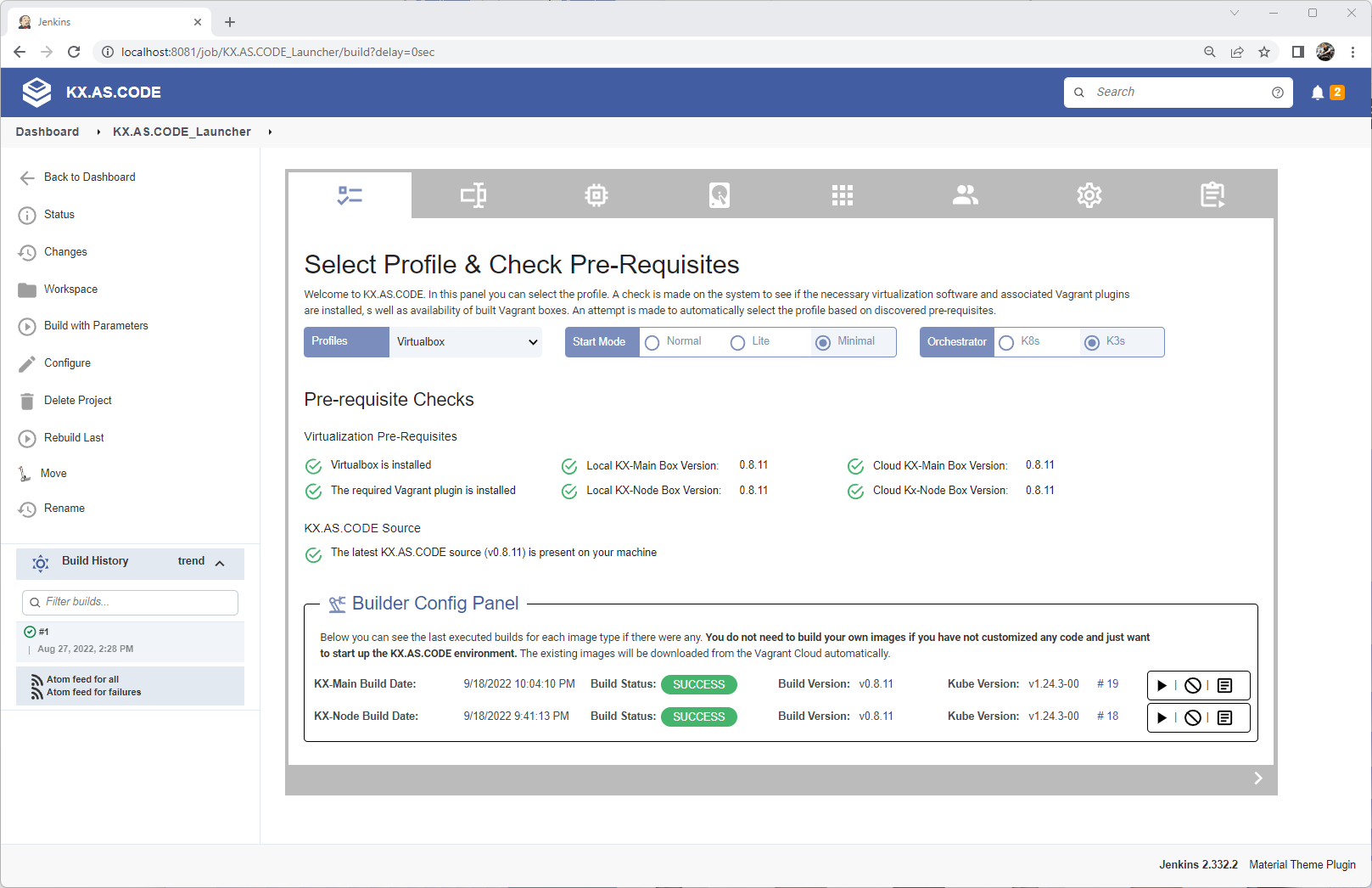
Jenkins based launcher for building and launching KX.AS.CODE
Configure your KX.AS.CODE instance using the Jenkins based launcher. On this screen you can select between K3s and K8s amongst others.
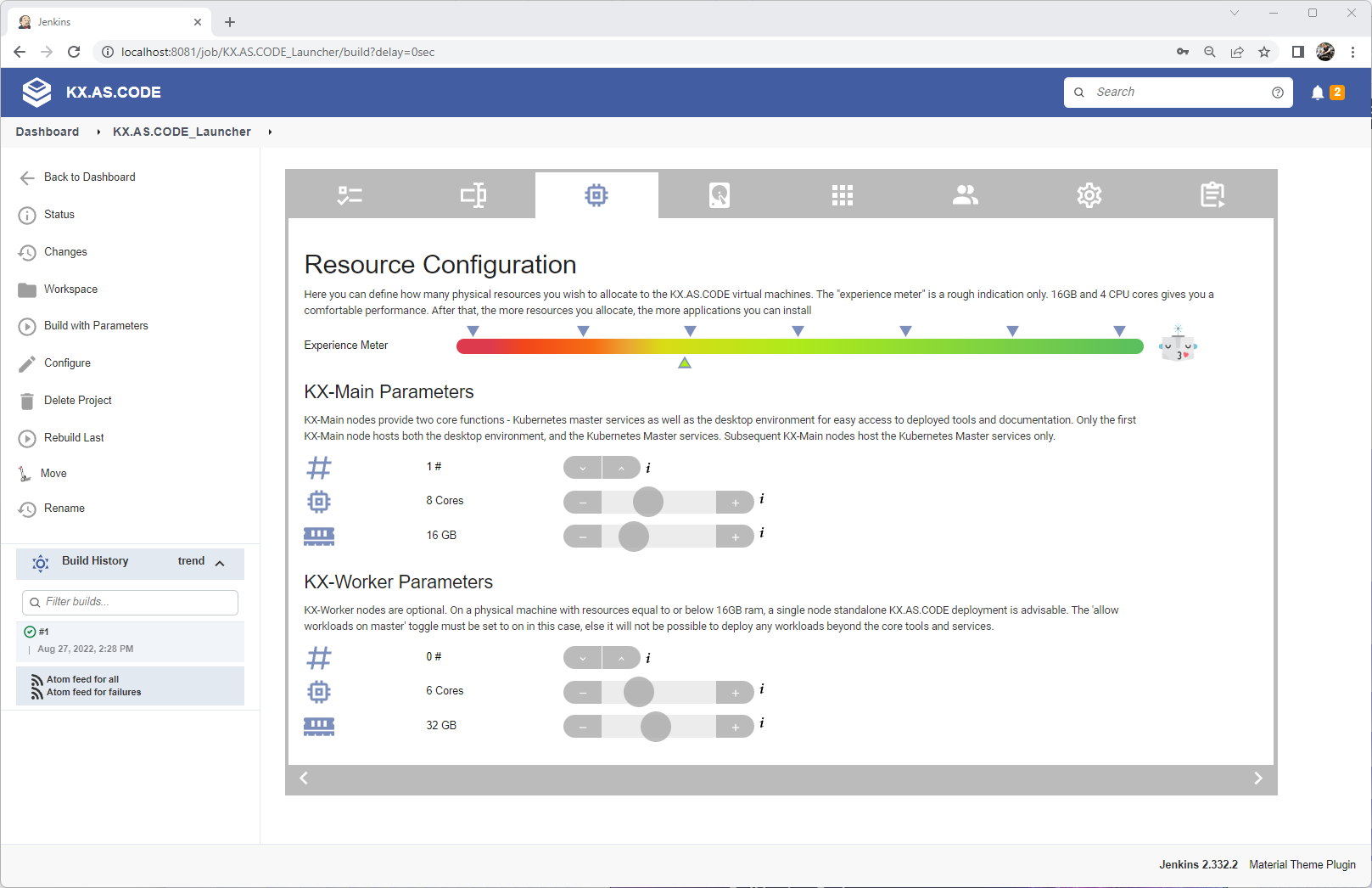
Hardware resource allocation for virtual machine(s)
Here you determine how much physical resource you want to allocate to the kx-main and the optional kx-worker node(s). The experience bar gives you a very rough indication as to the experience you may expect given the allocation.
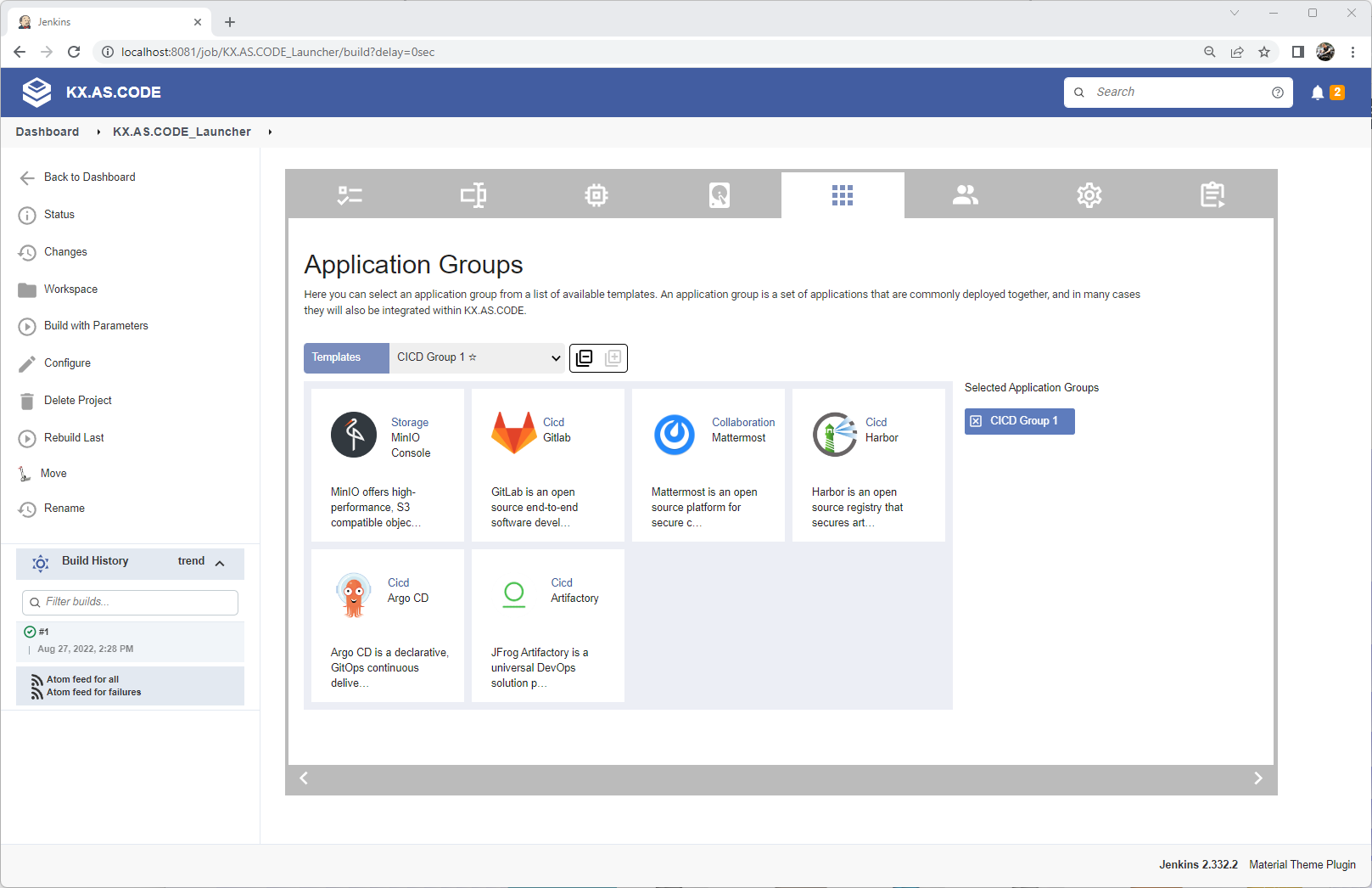
Optionally select application groups to install
You can also configure application groups that will be installed on first launch of KX.AS.CODE. More groups and individual applications can be added later.
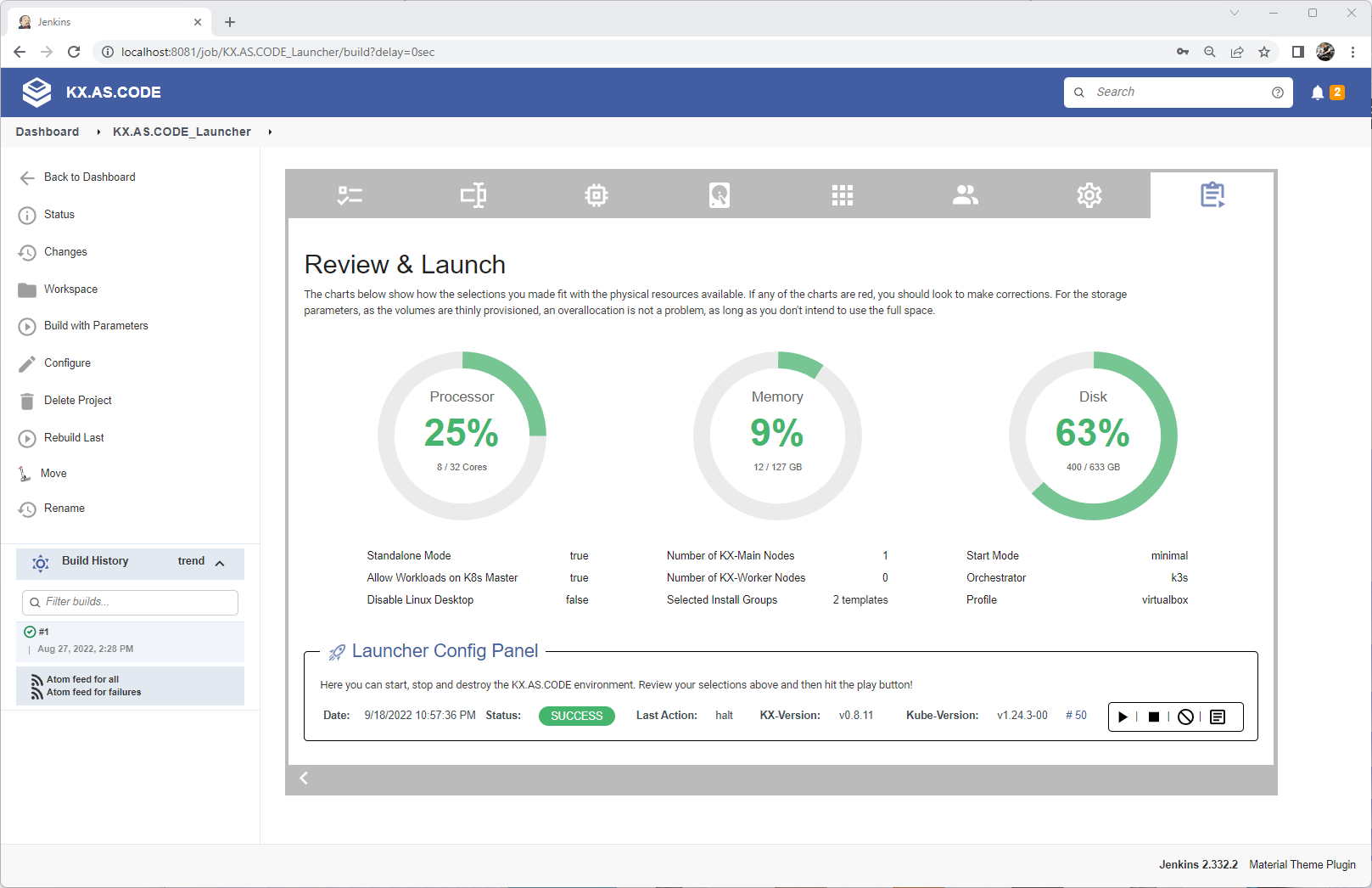
Review configuration and launch KX.AS.CODE
Once done configuring KX.AS.CODE in the launcher, you can review the settings and launch the KX.AS.CODE environment.
KX.AS.CODE login screen
Depending on whether the defaults were changed or not, you can either log in with your own user, or the default kx.hero.

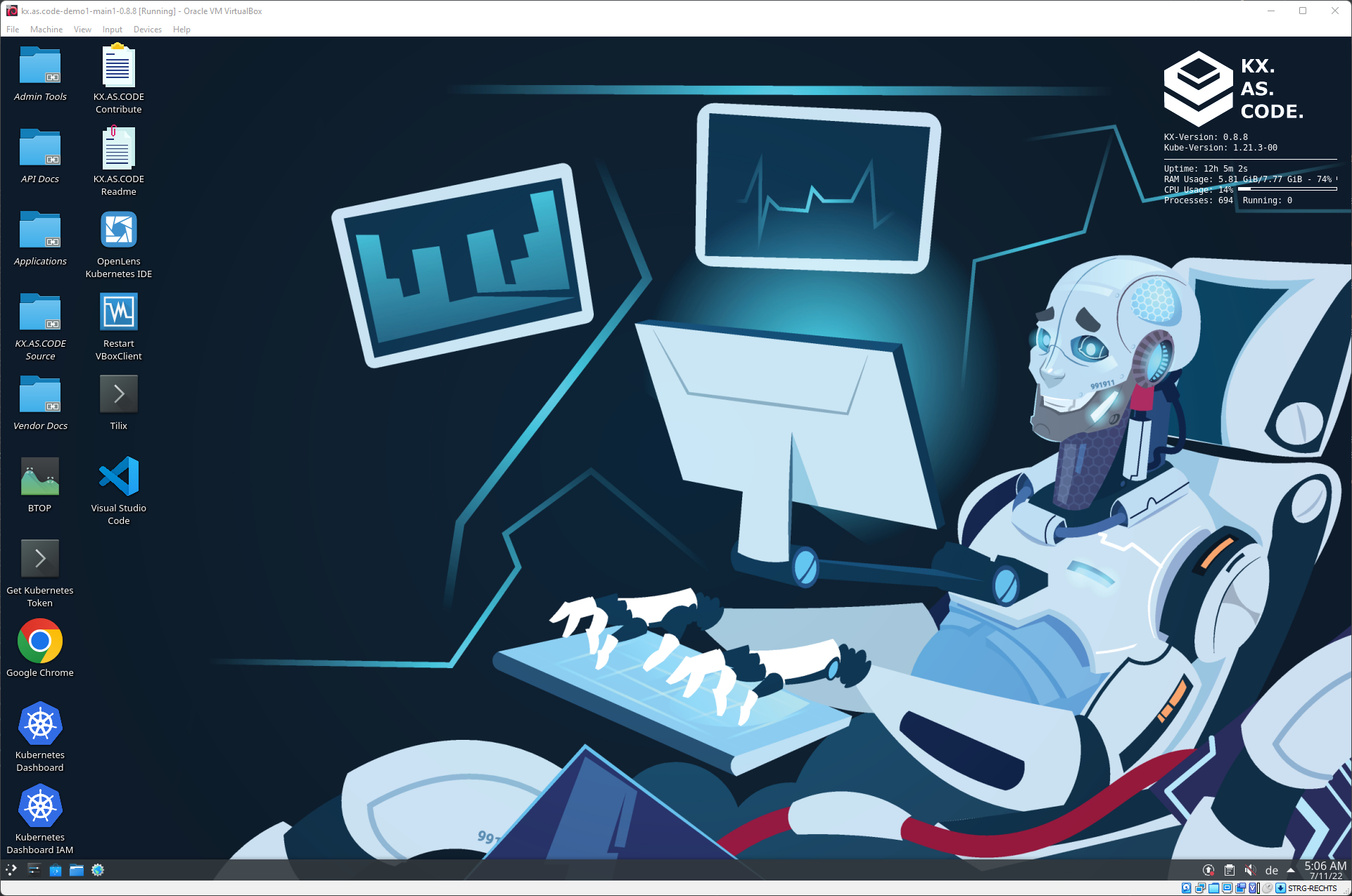
KX.AS.CODE Desktop
This is the home of KX.AS.CODE from where you can launch the deployed applications, read manuals, test API calls, administer the VM, and so on.

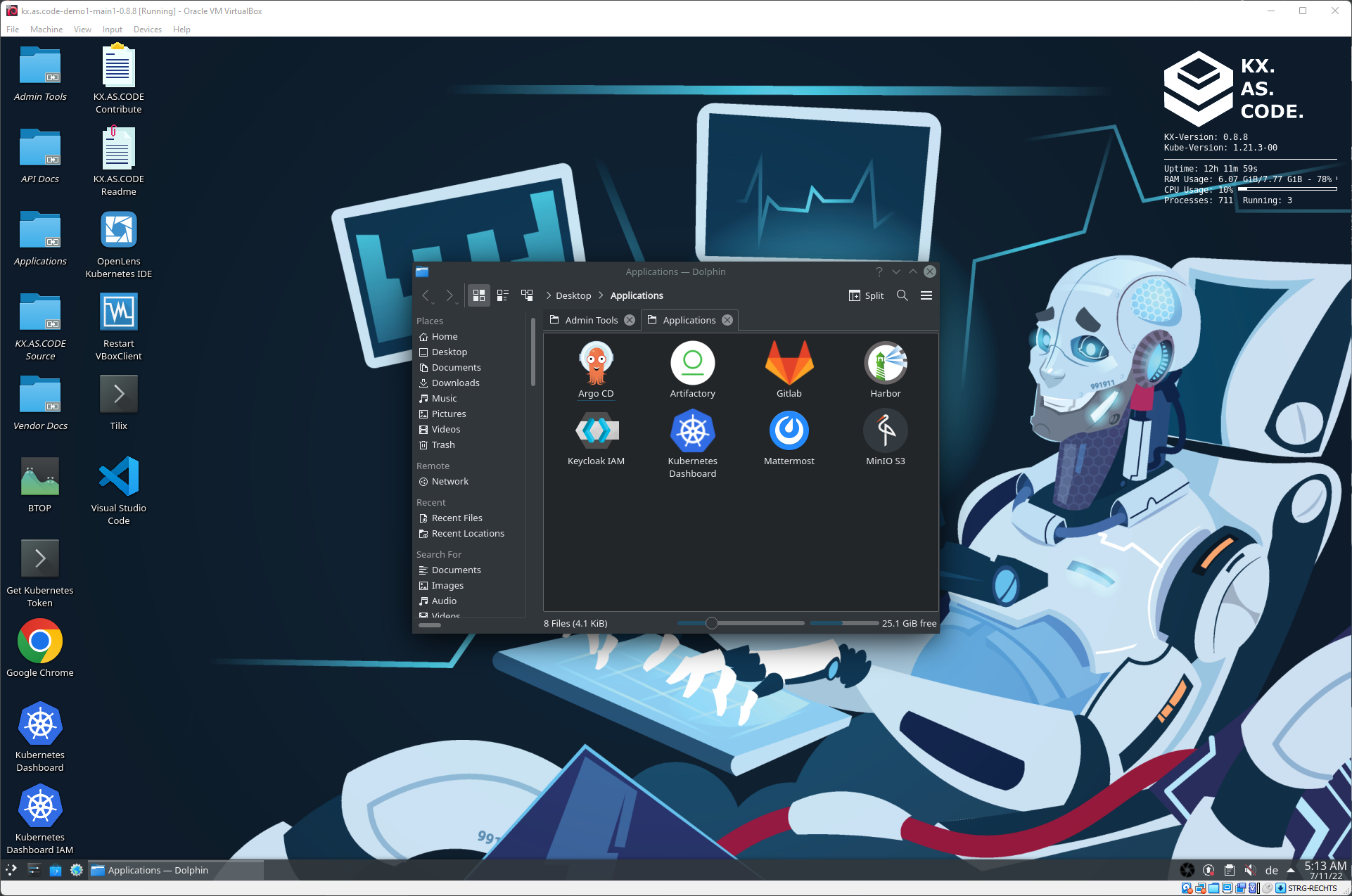
KX.AS.CODE installed applications, as selected in the KX.AS.CODE Launcher
The applications folder show the icons of the applications that have been installed so far and are available to launch. Use GoPoass to get the password for accessing the application.
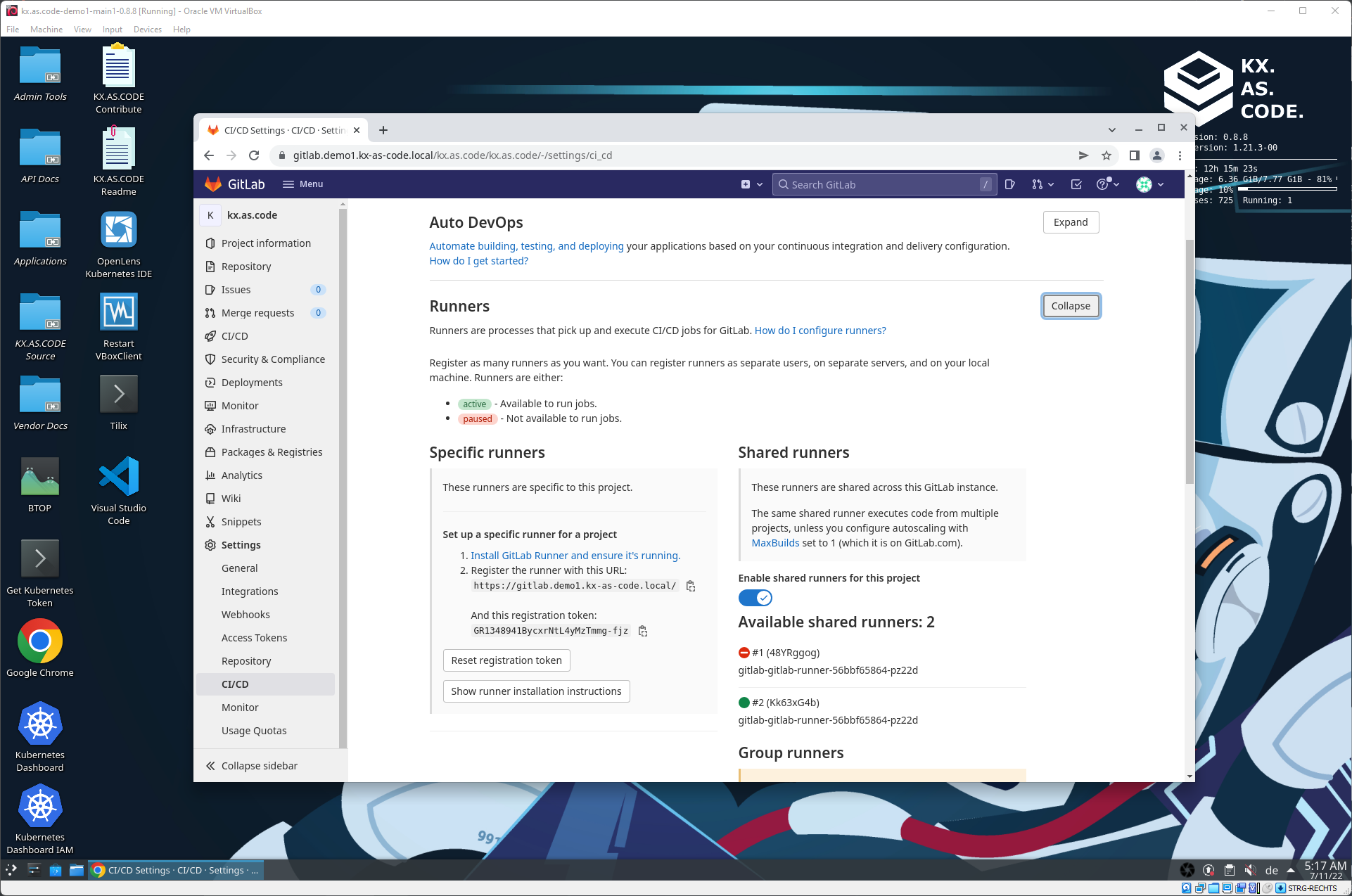
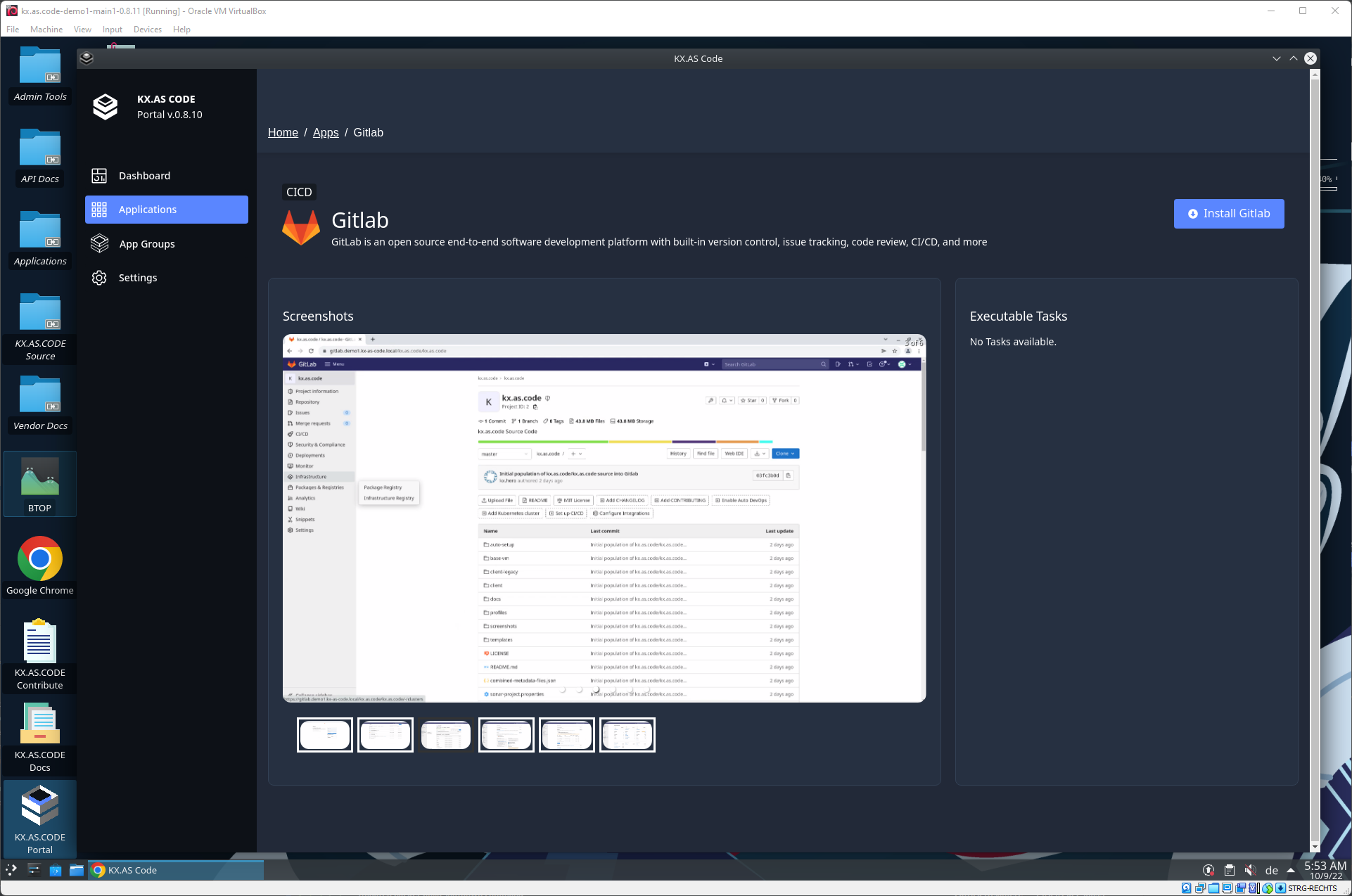
Gitlab Installed to KX.AS.CODE
Here an example Gitlab application that was installed via the KX.AS.CODE automated install scripts.
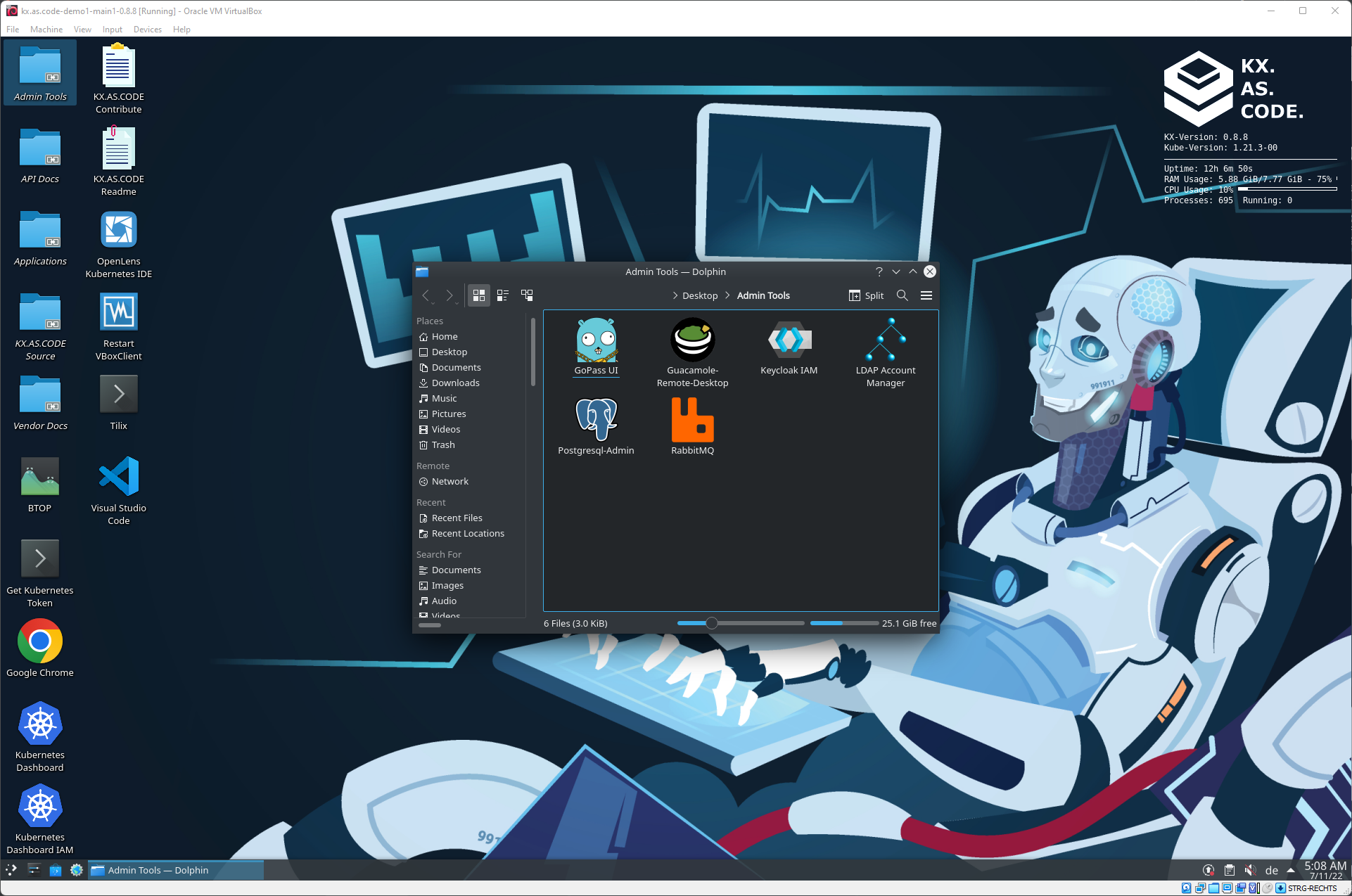
Administration Tools
The tools for administering some elements of KX.AS.CODE. More details will be published on the administration page (wip).
Application API Manuals
Since we are in the world of DevOps here, API documentation is important for automating any workflows. API documentation is automatically linked for all applications installed via KX.AS.CODE.
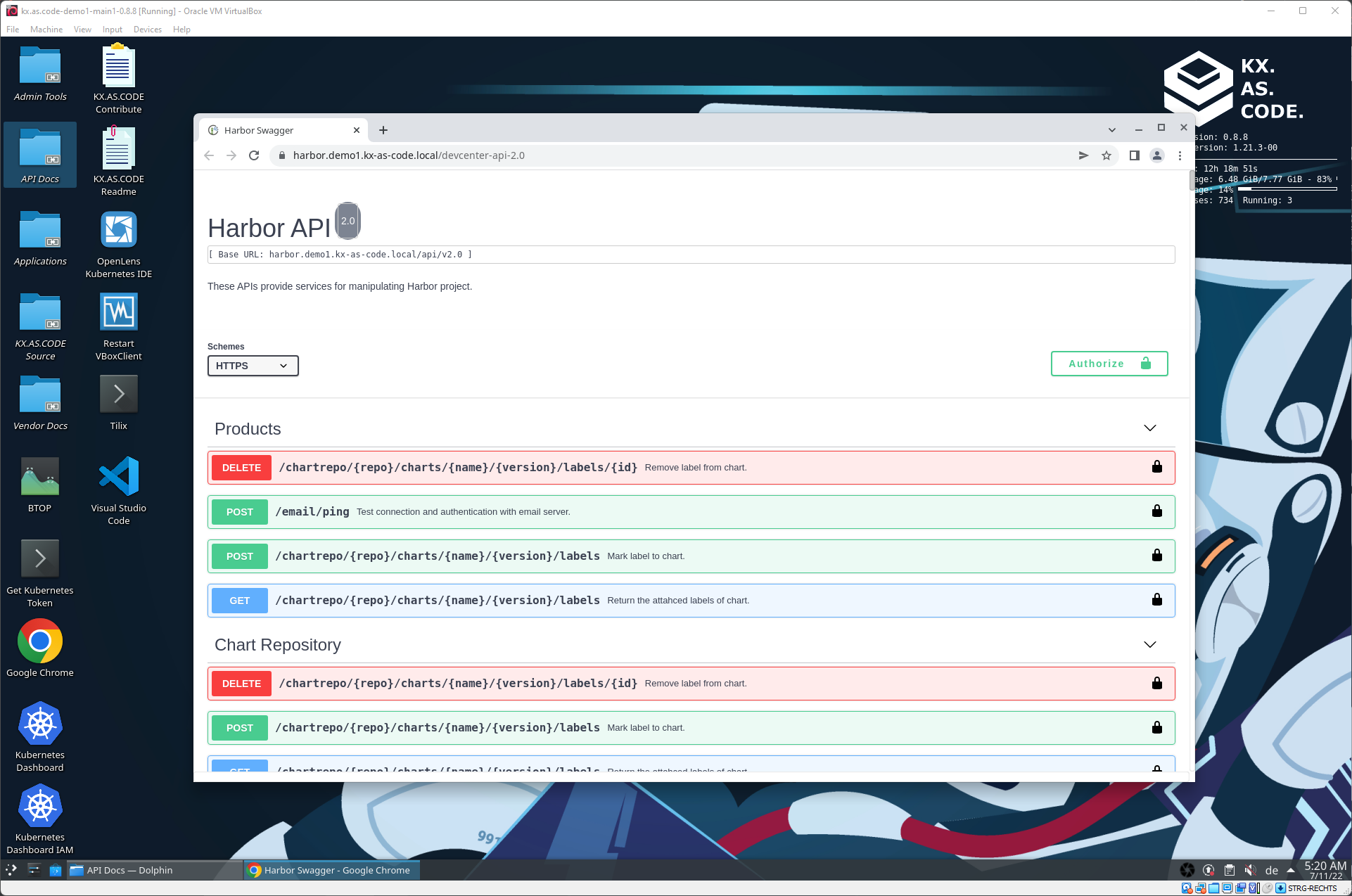
Harbor Swagger API
If an application has a Swagger endpoint, this is also accessible via the API docs folder.
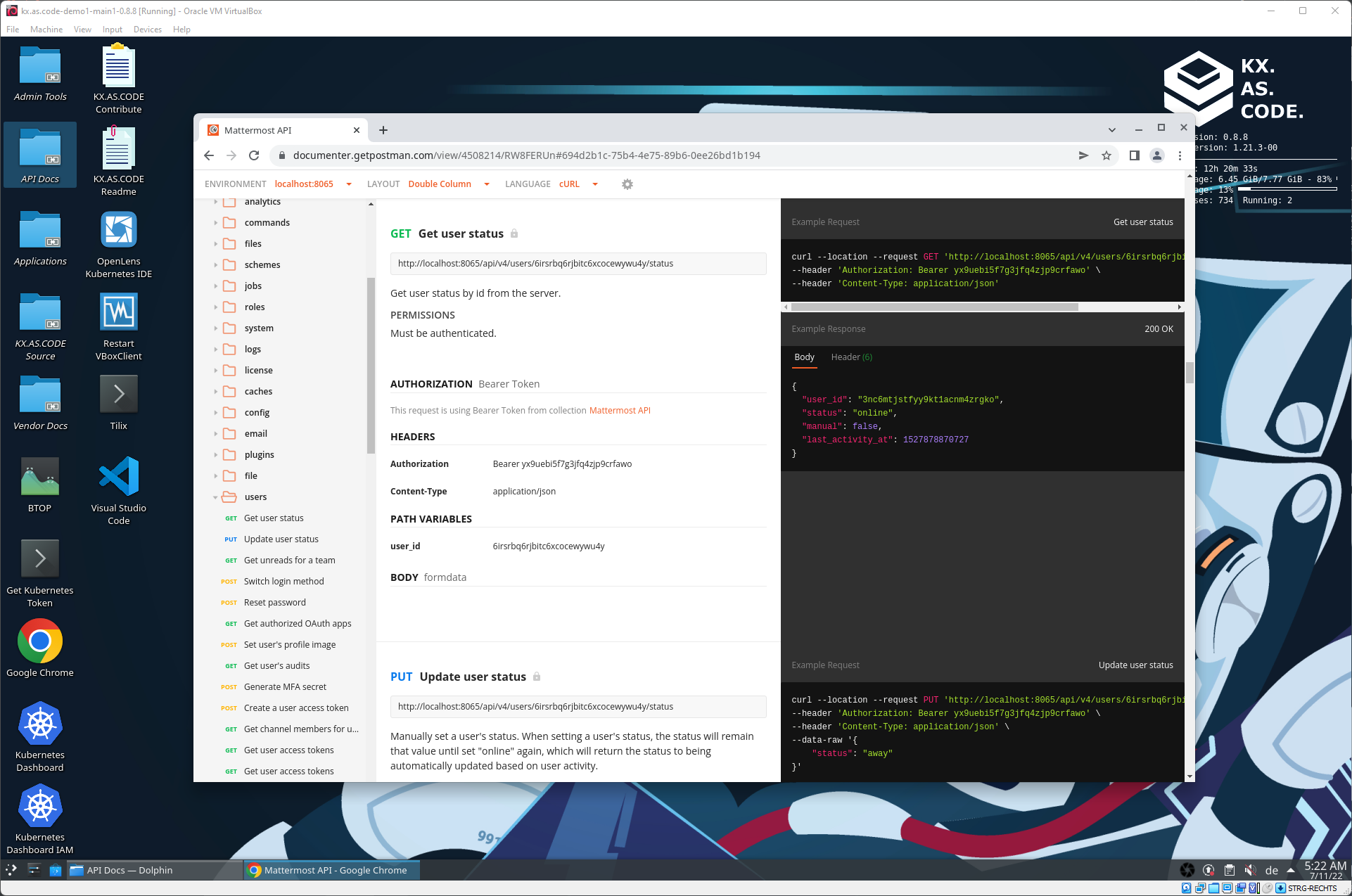
Postman API documentation
If an application has a Postman endpoint or public link, this is also accessible via the API docs folder.
Application Manuals
Administration and user manuals are useful if you are new to an application and want to read up on how it works.
Source code in VSCode
Since the original concept of KX.AS.CODE was all about sharing knowledge as code (it has since become so much more), a pre-configured VSCode is installed that includes all the KX.AS.CODE source code.

Credential Management with GoPass
All administration passwords for accessing all admin tools and applications are stored here. The passwords for the users are also available here.
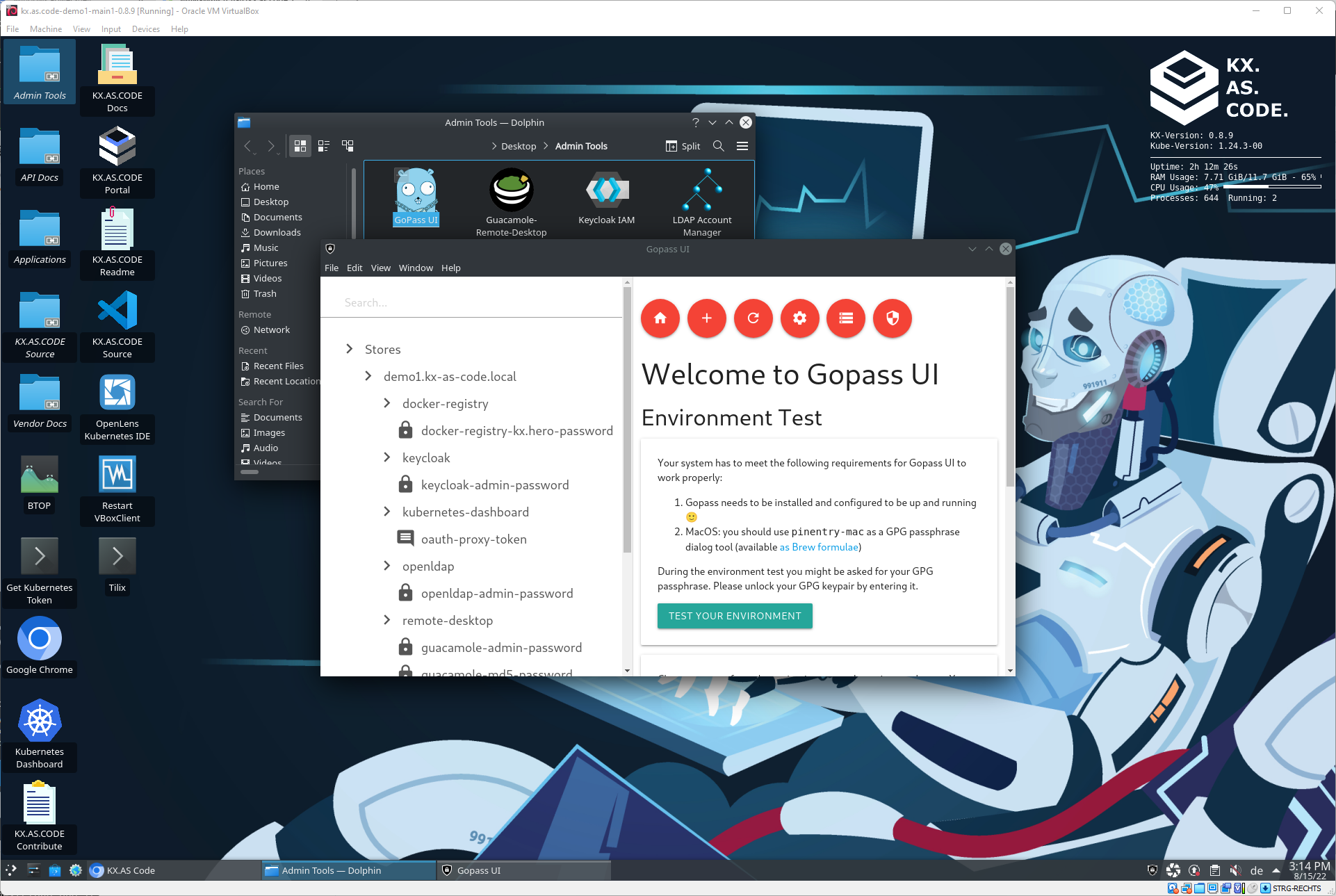
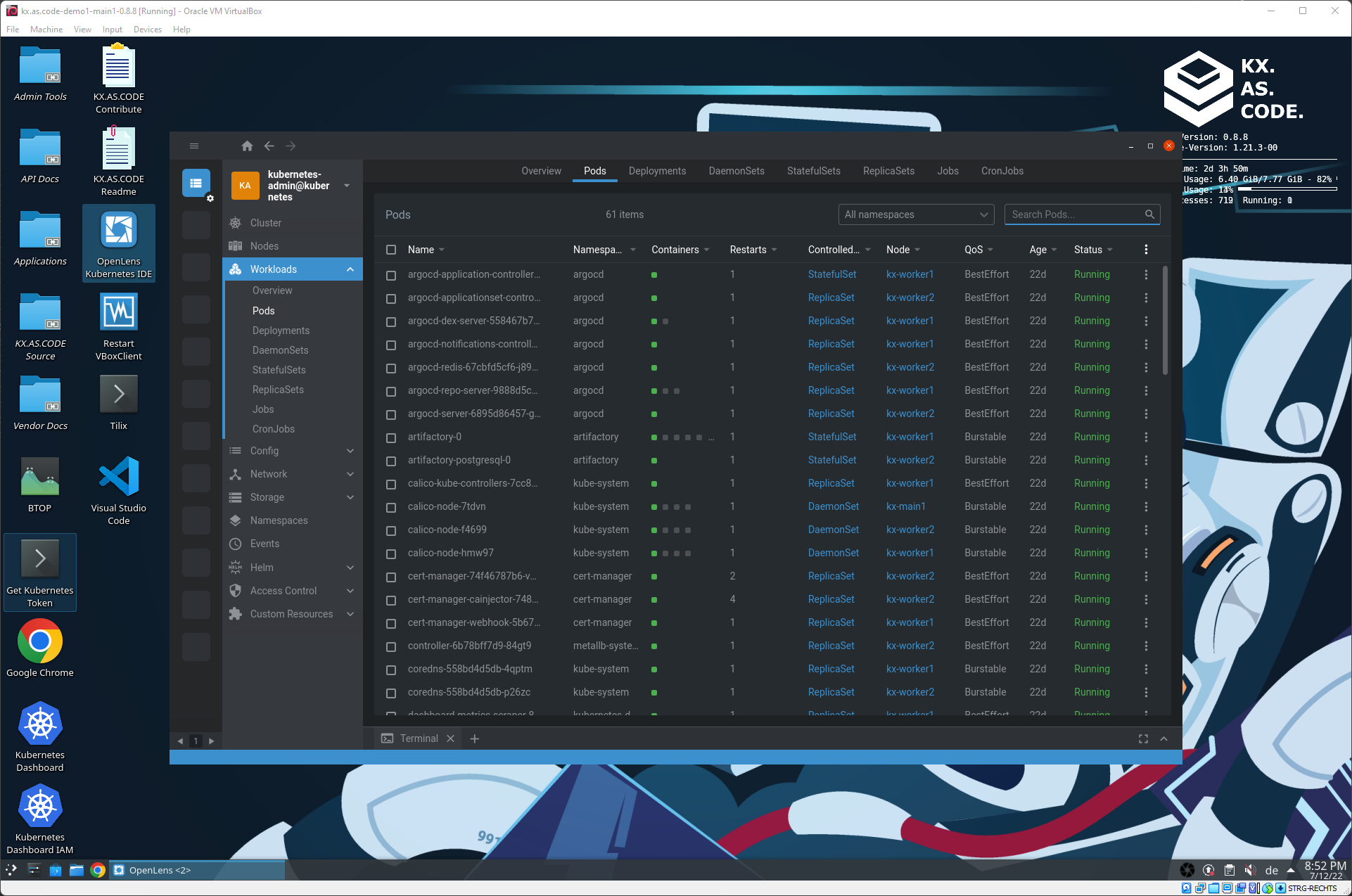
Kubernetes Management with OpenLens
OpenLens, known as the Kubernetes IDE, displays information about the running workloads in Kubernetes and their status. It is useful for debugging if there is an issue with any of the workloads.
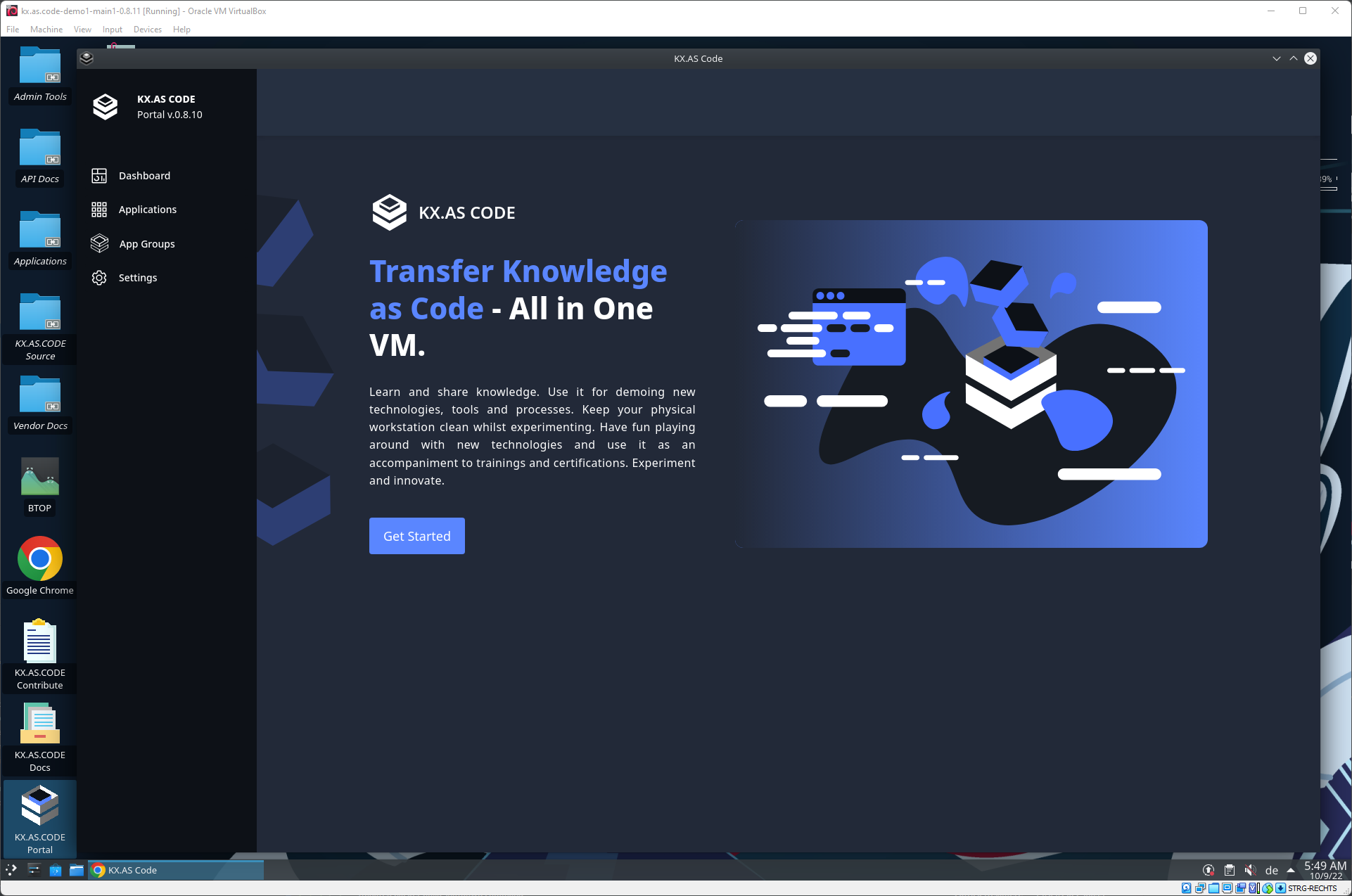
KX.AS.CODE Management with the KX.AS.CODE Portal (ALPHA)
The KX.AS.CODE portal makes adding and removing applications easier, and provides status on current installed items.
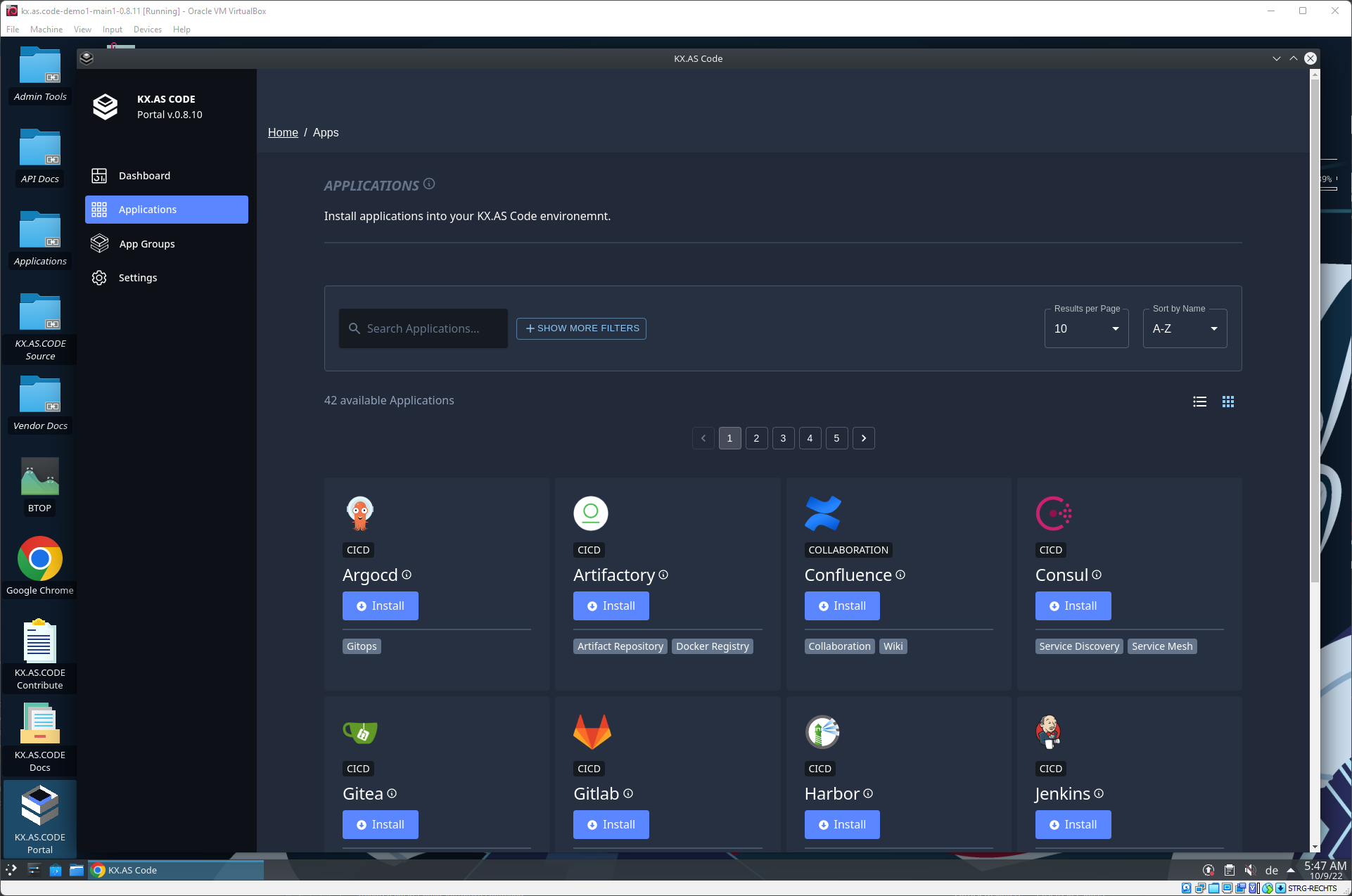
KX.AS.CODE Portal - App Store
Applications can be removed and added from the KX.AS.CODE Portal’s app store screen.
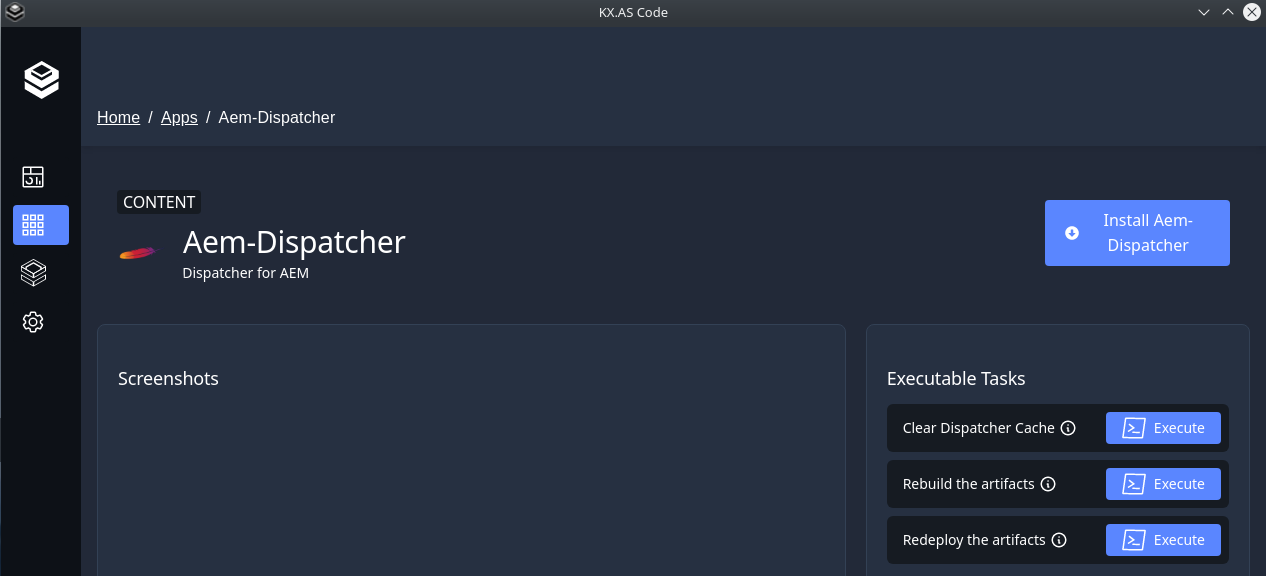
KX.AS.CODE Portal - Application Details
The application details screen shows more information about the application. It is also possible to execute tasks from this screen. In the future, this screen will also allow the user to enter values for input arguments.
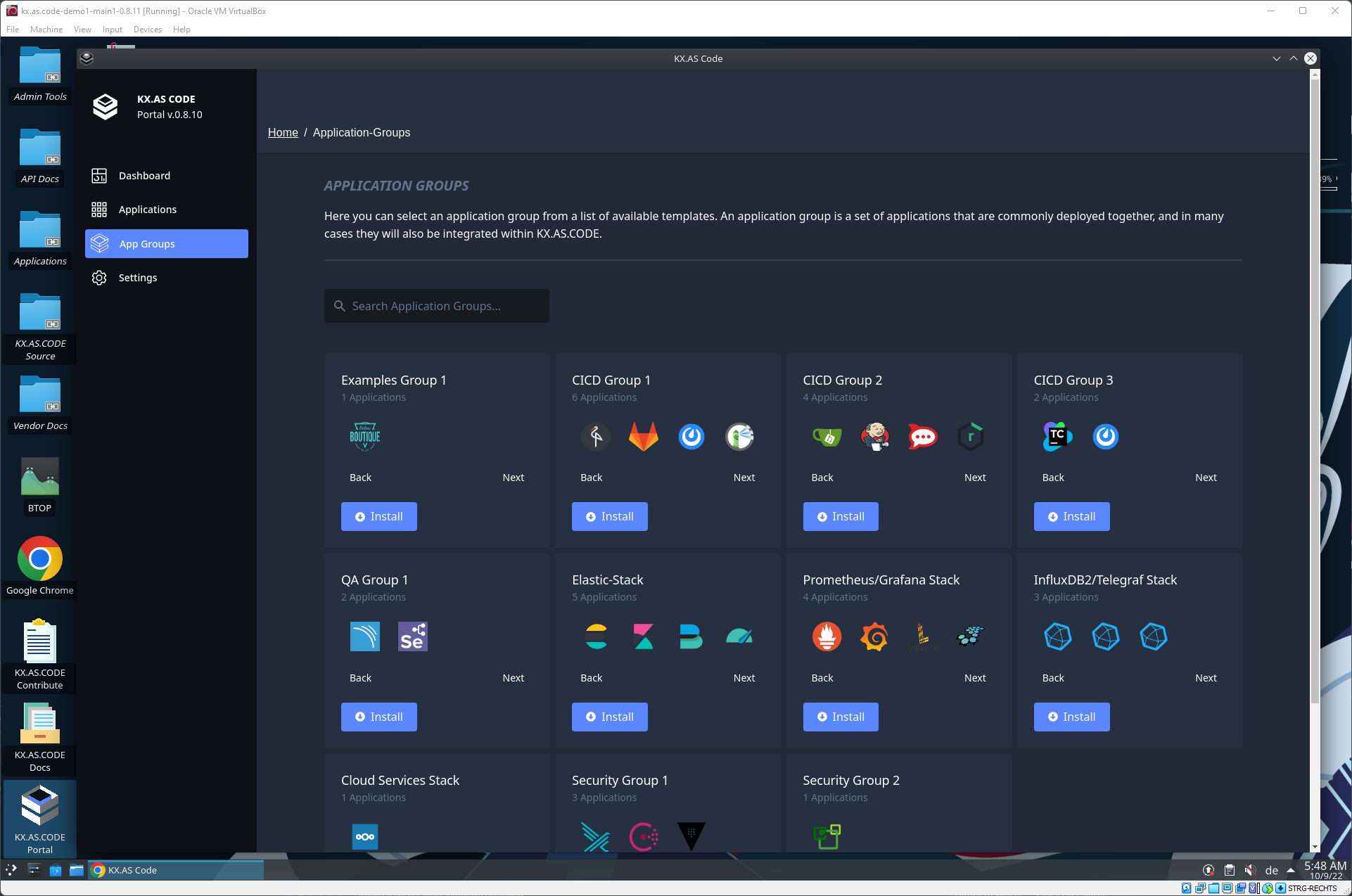
KX.AS.CODE Portal - Application Groups
Applications can be installed in integrated groups. This is still in development, so the install button currently does not execute the group installation. See the manual installations page, on how to install the groups manually without the portal.