Gitlab Integration with Jenkins
This page explains how the build trigger functionality can be enabled in ADOP/C between Jenkins and GitLab.
Introduction
Build trigger refers to Jenkins jobs being triggered when a change in the repository occurs, usually when someone pushes a change to the repository or creates a pull request.
Prerequisites
* GitLab instance running with root account access
* The following GitLab configuration when using ADOP/C or for components where the network communication for the components is internal
- Login to GitLab as root
- Click on the admin area by clicking on the wrench
- Click on Settings from the panel on the left and from the expanded sub-options click on Network
- Find the “Outbound requests” section and expand
- Tick the box which says “Allow requests to the local network from hooks and services”
- Click on Save
High Level Overview
The procedure to enable build triggers is as follows:
ADOP/C deployment already takes care of the first two points
- Generate a GitLab user token which serves as a form of authentication for a user who wants to access the GitLab REST API and save it in Jenkins credential store as type “Gitlab Credentials”
- Add Jenkins’s public key to GitLab so that Jenkins can clone repositories
- Configure Jenkins to communicate with GitLab for triggering using an access token
- Configure the Jenkins job to be triggered when a change to the repository occurs
- Set up your GitLab repository config so that it notifies Jenkins when a change happens and test
Procedure
Generate a GitLab user token which serves as a form of authentication for a user who wants to access the GitLab REST API
- This should have been configured during ADOP/C initialisation
- Login to Jenkins as an administrator
- From the vertical panel on the left click on Credentials
- Make sure that you can see a set of credentials with ID GitLab API token
Add Jenkins’s public key to GitLab so that Jenkins can clone repositories
- This should have been configured during ADOP/C initialisation
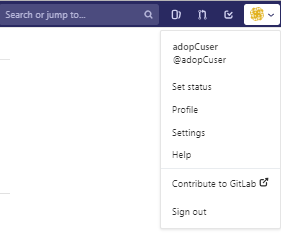
- In GitLab, go to your account settings by clicking on your account settings
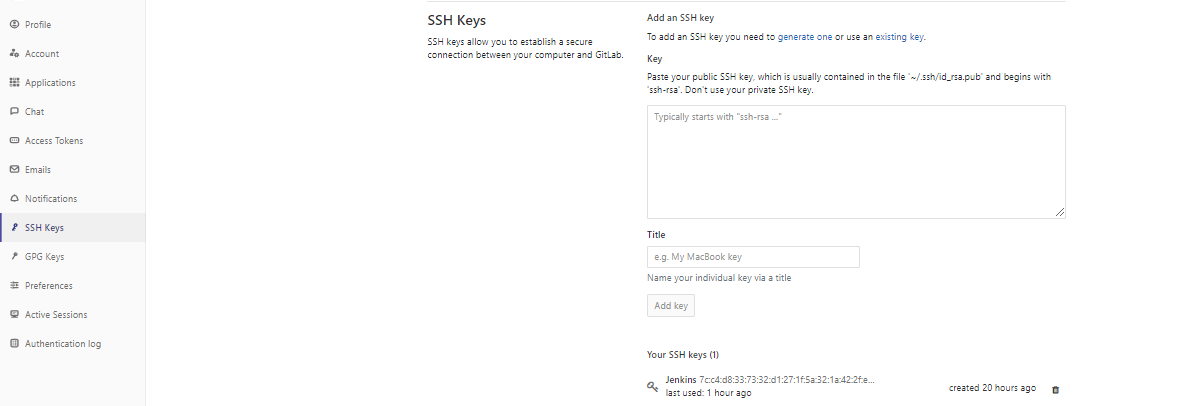
- Click on SSH keys and make sure that you can see Jenkins’s SSH key as follows
- If you cannot see the SSH key you can add it manually by pasting it the “Key” textbox, giving it a name and clicking on “Add key”. In ADOP/C, Jenkins’s public key can be found at
/jenkins/userContent/id_rsa.pub/*view*/
Configure Jenkins to communicate with GitLab for triggering using an access token
While in Jenkins as an administrator, click on Manage Jenkins from the vertical panel on the left hand side → Configure System
- Find the GitLab section
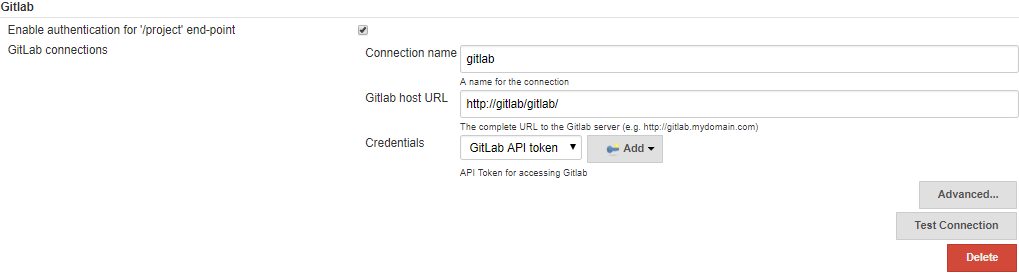
- Click on “Add”
- Configure the communication settings as follows
The host URL is http://gitlab/gitlab as within ADOP/C host names are used. IP addresses and ports can also be used e.g http://10.0.1.3:80/gitlab or e.g http://10.0.1.3:80 depending on the particulars of the setup.
The set of credentials Gitlab API token, is of type GitLab credentials and should have been added during ADOP/C initialisation
Configure the Jenkins job to be triggered when a change to the repository occurs
- Identify the Job you would like to be triggered
- Click on Configure
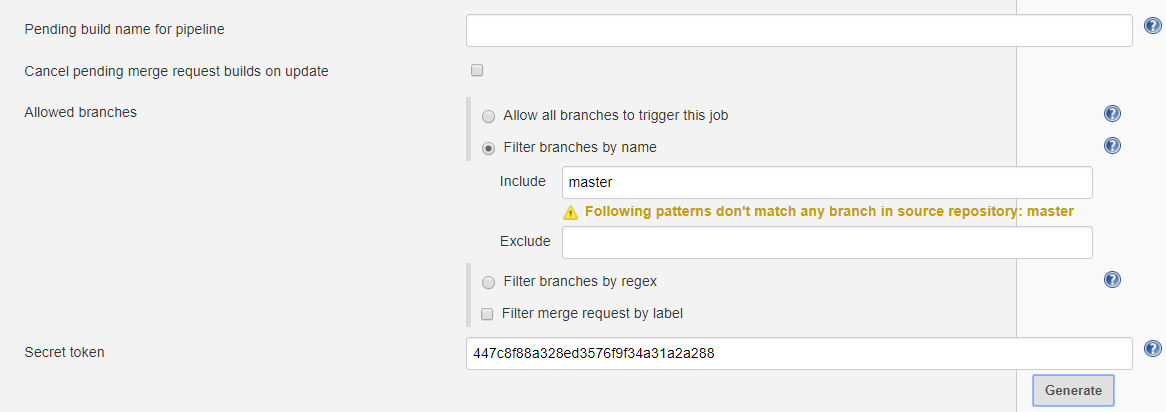
- Find the Build Triggers section
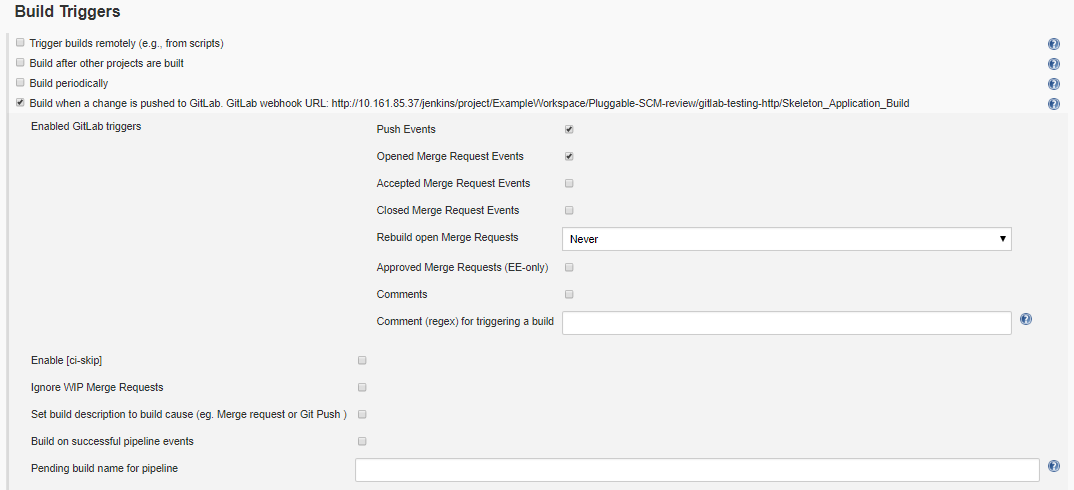
- Click on Advanced so that all settings become visible
- The configuration should look similar to
- Copy the webhook URL shown next to “Build when a change is pushed to GitLab. GitLab Webhook URL:” and save it somewhere
- Some of the configuration will be already be there as configured in the cartridge. For example, by including the line triggers scmProvider.trigger(projectScmNamespace, skeletonAppgitRepo, “master”) in the cartridge, the job will be configured to be triggered when a push is made to master (‘Push Events checkbox ticked’) or when someone merges a pull request. This is achieved through the pluggable-scm library which is included in ADOP/C. Feel free to tick/untick boxes as per your requirements
- Next to ‘secret token’, click on the Generate button in order to generate a token. Copy this token as it will be used in the next section where the GitLab side of the integration is configured.
** Info: You can specify a comma separated list of values of the branches which you want to the triggering to happen on or not to happen on. Regular expressions are allowed e.g “feature/*” **
Set up your GitLab repository config so that it notifies Jenkins when a change happens and test
- Find the repository for which you want to configure triggering for.
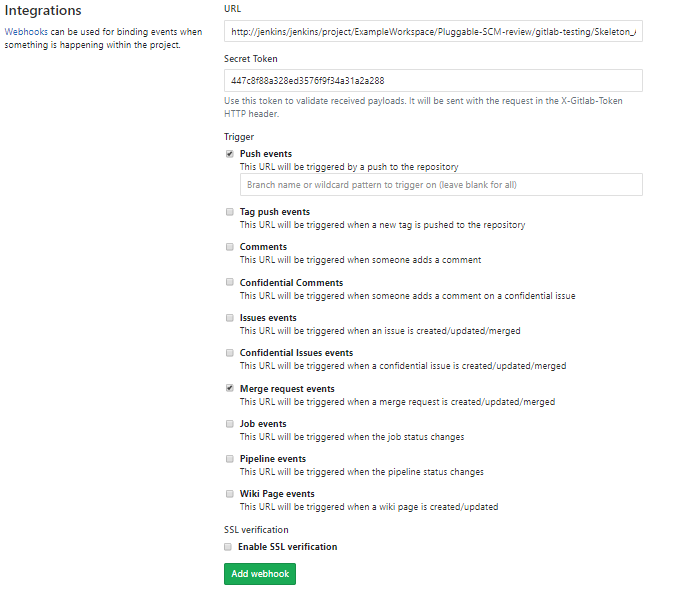
- In your project home, click on Settings ->Integrations
- Enter the URL copied in the previous section. Replace the IP with
jenkins:8080on the URL. For example, if the copied URL is http://10.0.1.3/jenkins/project/job-name, the URL should be http://jenkins:8080/jenkins/project/job-name - Enter the token copied in the previous section and tick the boxes as per your requirement
- Tick the checkboxes for the same triggers configured in the previous section
- The result should be similar to:
- Click on Add webhook
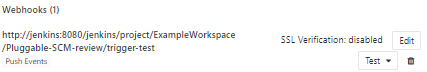
- In the same page, your webhook should appear under the Add webhook button as follows
- Click on Add webhook
- In the same page, your webhook should appear under the Add webhook button as follows
- Click on test and verify that a green banner shows up indicating that a connection was established and make sure that your job has started running
Resources
- A step by step tutorial outside the context of ADOP/C the can be found here. The same post has been reproduced in GitHub here.
- Jenkins DSL trigger functionality documentation