API Gateway Synchronization
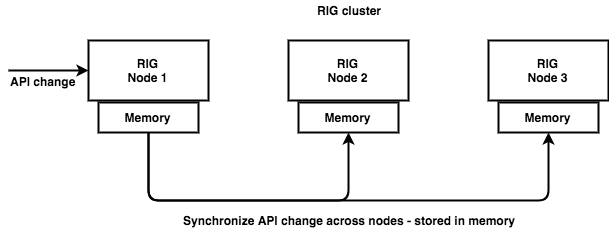
The reverse proxy configuration consists of API definitions, which are synchronized among RIG nodes (eventually consistent). API definitions, like everything else in RIG, are stored in-memory only, which makes accessing them very fast. The image below shows how a change to an API definition on any node will eventually spread to all other nodes.
Initial startup
The initial synchronization happens on RIG startup. Indeed, as long as one node has a JSON file with API definitions the configuration will be automatically spread among all nodes. In case there are two different JSON files found in the cluster, both are loaded and synchronized - eventually, all nodes have them configured. Note that the JSON file is only used at startup and is not used thereafter; for example, changes done to an API definition through RIG's API are not reflected in the file. Conflicts are resolved using several rules:
ref_number- Describes the version of the API definition. The higher the number, the newer the API and the higher the priority in the merging process.- Data comparison - compares the API definitions directly. If they are different, the API is also checked on other nodes. Finally, the version that is used on most nodes is determined to be current.
- If multiple versions of the API definition are used evenly among nodes then timestamps are compared and the newer definition is selected.
Runtime changes
You can change API definitions also during runtime via the REST API. Again, it's enough to change an API definition on single node and changes will be spread to the others. For this type of synchronization we use the same rules as above.