Avro Implementation Details
Apache Avro format as adapted by the Confluent Schema Registry:
# 0 - magic byte
# 1-4 - schema id - this is used by consumer to know which schema to use for deserialization
# 5-... - data
# Example
<0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 5, 3, 8, ...>
Overview
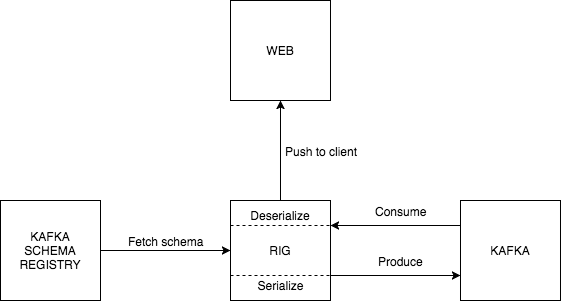
Adopting Avro for event (de)serialization is fairly straightforward. First you need to run an instance of the Kafka Schema Registry, which is a central store for all Avro schemas in use. As an event is consumed from Kafka, RIG fetches the corresponding schema from the registry and deserializes the event with it, caching the schema in the process (in memory). As for producing, RIG again retrieves and caches the schemas used for serializing events.
RIG as a Kafka producer
- producer evaluates if serialization is turned on by checking
KAFKA_SERIALIZERenvironment variable and if it's value isavro - If it is, creates headers for Kafka event by appending
ce_prefix for every field, exceptdatafield - binary mode- nested context attributes are stringified, since Kafka headers don't support nested values (this is common when using Cloud events extensions)
- after that, the
datafield is serialized using the schema name (function for getting schemas from registry is cached in-memory) - producer sends event with created headers and data (in binary format
<<0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 5, 3, 8, ...>>) to Kafka
If
KAFKA_SERIALIZERis not set toavro, producer sets onlyce_contenttypeorce_contentTypefor kafka event
RIG as a Kafka consumer
Event parsing is based on the Kafka Transport Binding for CloudEvents v1.0 implemented via cloudevents-ex. Check the Event format section.
Example 1: producing to and consuming from the same topic
In this example we'll have RIG send a message to itself to see whether RIG producing and consuming parts work correctly. The idea is that RIG produces a serialized event as a result to an HTTP request and, a few moments later, consumes that same event (and deserializes it correctly).
## 1. Start Kafka with Zookeeper and Kafka Schema Registry
KAFKA_PORT_PLAIN=17092 KAFKA_PORT_SSL=17093 HOST=localhost docker-compose -f integration_tests/kafka_tests/docker-compose.yml up -d
## 2. Start Rig
# Here we say to use Avro, consume on topic "rigRequest" and use "rigRequest-value" schema from Kafka Schema Registry
# Proxy is turned on to be able to produce Kafka event with headers (needed for cloud events)
docker run --name rig \
-e KAFKA_BROKERS=kafka:9292 \
-e KAFKA_SERIALIZER=avro \
-e KAFKA_SCHEMA_REGISTRY_HOST=kafka-schema-registry:8081 \
-e KAFKA_SOURCE_TOPICS=rigRequest \
-e PROXY_CONFIG_FILE='[{"id":"my-api","name":"my-api","versioned":false,"version_data":{"default":{"endpoints":[{"id":"post-myapi-publish-async","path_regex":"/myapi/publish-async","method":"POST","target":"kafka","topic":"rigRequest","schema":"rigRequest-value"}]}},"proxy":{"use_env":true,"target_url":"KAFKA_HOST","port":9092}}]' \
-e LOG_LEVEL=debug \
-p 4000:4000 -p 4010:4010 \
--network kafka_tests_default \
accenture/reactive-interaction-gateway
## 3. Register Avro schema in Kafka Schema Registry
curl -d '{"schema":"{\"name\":\"rigproducer\",\"type\":\"record\",\"fields\":[{\"name\":\"example\",\"type\":\"string\"}]}"}' -H "Content-Type: application/vnd.schemaregistry.v1+json" -X POST http://localhost:8081/subjects/rigRequest-value/versions
## 4. Send HTTP request to RIG proxy
# Request will produce serialized Kafka event to Kafka
curl -d '{"id":"069711bf-3946-4661-984f-c667657b8d85","type":"com.example","time":"2018-04-05T17:31:00Z","specversion":"0.2","source":"\/cli","contenttype":"avro\/binary","data":{"example":"test"}}' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST http://localhost:4000/myapi/publish-async
## 5. In terminal you should see something like below -- in nutshell it means event was successfully consumed, deserialized and forwarded to UI client
12:35:36.235 module=Avrora.Storage.Registry [debug] obtaining schema with global id `1`
12:35:36.236 module=RIG.Tracing [debug] private mode, remove tracestate.
12:35:36.237 module=Rig.EventStream.KafkaToFilter [debug] %{:__struct__ => Cloudevents.Format.V_0_2.Event, :contenttype => "avro/binary", :data => %{"example" => "test"}, :extensions => %{"rig" => %{"correlation" => "NTd2PR-TnLX00m4qYT-5fiSvuI_ymOvikja50kMPEYkezFkMcwhBY33rCgYCgKnlSSozVbYQZhWxqR8=", "headers" => [["accept", "*/*"], ["content-length", "188"], ["content-type", "application/json"], ["host", "localhost:4000"], ["user-agent", "curl/7.64.1"]], "host" => "localhost", "method" => "POST", "path_regex" => "/myapi/publish-async", "port" => 4000, "query" => "", "remoteip" => "172.19.0.1", "scheme" => "http"}, "traceparent" => "00-b068f0d83c5938fa6d0fb8c21959edf6-0ee83bcb44fb61e0-01"}, :id => "069711bf-3946-4661-984f-c667657b8d85", :schemaurl => nil, :source => "/cli", :specversion => "0.2", :time => "2018-04-05T17:31:00Z", :type => "com.example", "traceparent" => "00-86567e8c4b4cdb6c7f052b0f627959f9-c00644b7954af2fd-01"}
Example 2: Kafka schema Registry CLI
To check if it works also with native serializer we can leverage the CLI shipped with the Kafka Schema Registry image.
# 1. Get inside Kafka Schema Registry container
docker exec -it kafka-schema-registry bash
# 2. Start native consumer with Avro
kafka-avro-console-consumer --topic rigRequest \
--bootstrap-server kafka:9292 \
--property schema.registry.url='http://kafka-schema-registry:8081'
# 3. Send HTTP request to RIG proxy - same request as before
curl -d '{"id":"069711bf-3946-4661-984f-c667657b8d85","type":"com.example","time":"2018-04-05T17:31:00Z","specversion":"0.2","source":"\/cli","contenttype":"avro\/binary","data":{"example":"test"}}' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST http://localhost:4000/myapi/publish-async
# 4. Now there should be message also in this consumer
{"example":"test"}